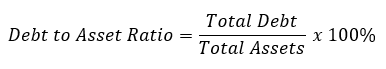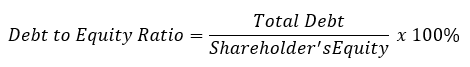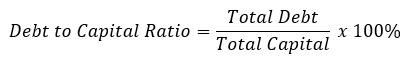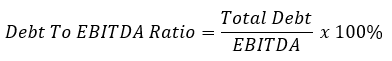- Understanding Business Valuation and Fair Valuation
- An Introduction to Investing in Start-ups
- Crafting a Winning Business Plan
- Investment Payback Period And What You Need to Know About It
- Unveiling the Power of Financial Modeling
FinModelsLab has created a fancy but informative dashboard to visualize the strengths and weaknesses of your business by simply switching Annual Financial Performance Dashboard & Financial Dashboard. A well-constructed template is designed for users without advanced Excel skills. Just enter the numbers in the appropriate cells and run the dashboard smoothly having the numerical and graphical presentation of business key performance indicators.
After reading this article, you should be Apple to learn:
- What is Financial Debt Ratio
- Type of debt ratio
- Uses of the debt ratio
- Importance of the debt ratio
- Limitation of the debt ratio
- FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is debt ratio
The debt ratio represents the total liabilities of the organization as a percentage of its assets. Debt ratios indicate the amount of debt an organization has used to finance its operations. It also indicates the entity’s ability to repay its liabilities. Investors and financiers/lenders look at debt ratio for overall risk assessment when investing or lending to an organization. The entity having a higher debt ratio is more risky investing in stocks and loans. Debt used by an organization to finance operations can be beneficial compared to equity investment if the gains generated are more than the interest incurred on the debt. The company having a debt ratio above 1.0 (100%) shows that the company is higher than its assets.
Commonly used debt ratios
There are various debt ratios used by business managers, analysts, equity investors or financing institutions.
Here are some of the debt ratios:
- Debt to Assets Ratio or Capitalization Ratio: This ratio shows the percentage of the organization’s assets that are funded using debt. Creditors use this ratio to determine the company’s liabilities and ability to repay while considering extending additional loans to the company. Although investors use such a ratio to assess the solvency of the company, it means whether the company will be able to meet its current and future obligations and the return on investment.
- Debt to Equity Ratio: This ratio is more reflective of the capital structure of the company. The capital of the company includes equity plus debt. This ratio gives the investor an idea of whether or not to invest in such a company. In case the debt ratio is higher, there may be bankruptcy risk of default by the company.
- Debt to ebitda ratio: EBITDA refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. This ratio is to determine the revenue generated by an organization available for debt payment before meeting interest, taxes, amortization and amortization charges. The debt repayment capacity of the organization is assessed by this formula. A higher ratio indicates that the company has too heavy a debt burden.
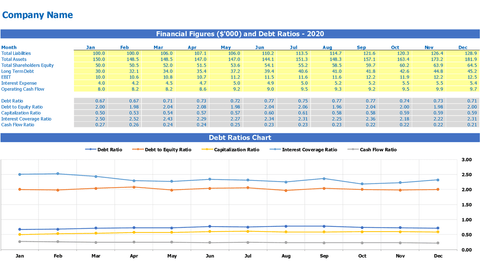
IMPORTANT NOTE: Check out our free designed Debt Ratios Excel Template Calculator In Excel and Google Spread Spread Sheet which calculates ratios without having Excel skills. You just need to insert quantities in the yellow cells and see the monthly ratios.
Assets, equity and liabilities used in financial debt ratios are taken from the balance sheet and therefore you may also be interested in reading our article on balance sheet. Also check out our free specially designed Monthly Balance Sheet and Annual Balance Sheet This helps you prepare the balance sheet by simply entering the numbers in the yellow highlighted cells.
Download Excel Template Calculator Debt Ratios in Excel
Uses of debt ratios
Financial debt ratios are calculated and used for the valuation of an entity to:
- Assess the company’s leverage and capital structure and the Company’s ability to meet its financial obligations. These ratios are generally compared to industry standards and higher than a similar comparable entity, the company is considered to have a high debt burden.
- The ideal debt ratio depends on the nature of business and industry standards. Debt ratio below 1.0 is considered safer by investors and loans, while ratio above 2.0 is more risky. However, when evaluating debt ratios, it is important to consider industry standards and norms, for example, average average debt to equity ratios in livestock were 0.04, while that in banking it was 8.46 in the United States based on FY-2012.
- Generally, equity has a higher cost than the cost of debt, therefore, these ratios provide business owners with guidance to raise the fund through debt financing and whether the return on debt is higher that the cost of debt, performance and profitability of the company can be improved.
Importance of debt ratios
Company stakeholders analyze debt ratios to understand the company’s capital structure, solvency and debt repayment capacity. The business owner, manager, investor, and lender analyze these investment and financing ratios.
Here is the usage on stakeholder reports:
- Business leaders use such a ratio while making a financing decision, whether to finance the operations of the business through its own funds or to borrow funds. The cost of financing is considered to achieve better results. Debt can improve business profitability and return on investment if used appropriately. Business leaders also assess this ratio to assess its needs to generate funds among the options available in equity and debt. Managers also compare the debt ratio with the prior period to take timely corrective action by maintaining investors and lenders.
- Equity Investors Compare the company’s debt ratios with other companies and industry standards to analyze investment risk before making any decision regarding equity investment. A higher debt ratio indicates the riskier investment and investors can negotiate a higher return on the additional investments.
- Banks/Creditors Also uses debt ratios when granting a loan to a business or extending credit facility. Debt ratios are high, risk the company and the ability to repay the business. Lenders generally charge higher interest rates while lending loans at higher debt ratios. Although the ratio is reduced, the more confidence banks/creditors have that their loans will be repaid.
These ratios also represent the liquidity of the company and the solvency of the company and can indicate the continuation hypothesis. If the company has higher debt ratios, it may indicate the ability of its obligations to deteriorate and bankruptcy.
Debt ratio limitations
Although debt ratios are effective tools for assessing company creditworthiness and capital structure, it has certain limitations and cannot be used in standalone/isolation to make a business decision.
Some of these limitations are explained below:
- Due to the involvement of multiple variables, valuation information may not be available in the financial statements and in-depth analysis may be required
- These ratios cannot be used in isolation and should compare to the relevant comparable industry prior period information.
- Share price volatility also impacts the accuracy of the analysis of corporate debt ratios and may lead to an erroneous result.
- These ratios are not uniform across the industry and should focus on industry-specific norms and standards.
Despite the fact that these ratios provide a better analysis of the company’s liquidity and solvency situation, such ratios cannot be used in isolation for decision-making by stakeholders.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q. Is the debt ratio an accounting concept?
Q. Is a higher debt ratio bad for business?
Q. What is the ideal ratio?
A. The ideal debt ratio depends on the business nature of the company. Generally, the debt ratio in the range of 0.3 to 0.6 is considered good by the investor. In the event that the debt ratio increases more than 0.6, the company may face challenges obtaining an additional loan, either the lender charges higher rates for associate risk
[right_ad_blog]