- Home
- Sales and revenue
- Running costs
- Financial
Welcome to our blog on “How to Build a Financial Model for a Frozen Food Store”. As a frozen food store owner, it is important not only to understand your income and expenses, but also to estimate your financial performance in the future. A financial model allows you to make projections based on your company’s past and current financial data, and helps make informed decisions about your business. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the key elements involved in building a financial model for a frozen food store, including revenue and profit models, financial planning, forecasting, and metrics.
Frozen Food Store Revenue and Sales Forecast
As part of the Frozen Food Store financial model, revenue and sales forecasts are a crucial part. This is to forecast the sales that would generate revenue for the store. This is done based on multiple growth assumptions such as launch date, sales ramp-up time, walk-in traffic and growth assumptions, customer and purchase assumptions, and seasonality of sales.
The launch date is the date when the store will open its doors to customers, and the sales ramp-up time is the time to reach target sales. The traffic and walk-in growth assumptions will guide the number of customers the store would attract in the early stages. Customer and purchase assumptions will guide the amount spent by each customer and the number of customers. Sales seasonality will guide how the store operates during peak and non-peak seasons. All these factors play a vital role in frozen food store revenue and sales forecast.
Frozen food store launch date
Choosing the right launch date for your frozen food store is a crucial first step in your financial planning. This affects your Frozen Food Store Financial Forecast and Frozen Food Store Financial Projection significantly.
When selecting your business launch date, weigh all the factors carefully. These may include local seasonality, competitor activity and the time required to complete preparations. You need to adjust your spending projections and revenue model based on the launch opportunity.
Tips & Tricks:
- Consider launching your business during peak seasons when sales are generally higher.
- Don’t forget to factor in the time required to acquire products and equipment, as well as any necessary licenses and permits.
- Work closely with your team and advisors to ensure a successful launch.
It’s important to remember that your launch date is just the beginning. Once your frozen food store is up and running, you will need to continue to monitor your frozen food store financial performance and adjust your financial plan as needed. By doing so, you can improve your Frozen Food Store Financial Management and increase your overall Frozen Food Store Financial Metrics .
Frozen food store ramp up time
When starting a frozen food store , forecasting sales is crucial for financial planning and management. To accurately forecast sales, it is important to consider the ramp-up time to reach the sales plateau.
The sales ramp-up period is the time it takes for a new frozen food store to reach its maximum sales potential. This period is essential for forecasting sales and determining the store’s financial projections. In the frozen food industry, the ramp-up period can reach six months.
Tips & Tricks:
- Conduct market research to understand your target audience and competition
- Factor in location and proximity to potential customers
- Build a strong brand and marketing strategy to attract customers
- Offer promotions and discounts to encourage new customers to come back
- Maintain high quality products and customer service to retain customers
By understanding the ramp-up period for a frozen food store and using financial analysis and forecasting, a business owner can effectively plan and manage finances for long-term success.
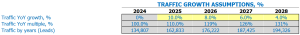
Frozen food store appointment traffic shots
After the average daily traffic spike-in-in-in period Visitors to a frozen food store can vary greatly weekdays. For example, Mondays and Tuesdays are usually slow days, averaging around 50 visitors per day. Wednesdays and Thursdays see more traffic with an average of 80 visitors per day, while Fridays, Saturdays and Sundays are the busiest days with around 120 visitors per day.
Having a good understanding of these traffic inputs is essential to building a solid financial model for a frozen food store. By knowing the number of daily visitors for each day of the week, the store’s revenue and profit models can be analyzed and optimized accordingly. It is important to consider the busiest and slowest days, as well as seasonal fluctuations, to create accurate financial projections and predict future growth.
The average traffic growth factor-in-in-in Over the next few years, another important entry. This number can be influenced by many factors, such as competitors opening a store or implementing new marketing strategies. The model will use this growth factor to calculate future walk-in traffic for each day of the week over a five-year period.
By considering these traffic inputs, a frozen food store can make informed financial decisions and ensure long-term financial success.
Tips & Tricks:
- Keep track of the daily number of day-of-the-week visitors to better understand customer behavior patterns.
- Consider investing in marketing campaigns or promotions during slow days to drive traffic.
- Be aware of seasonal fluctuations and how they can impact visitor numbers and revenue.
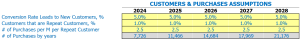
Frozen food store visits for sales conversion and sales inputs
In our frozen food store, we have seen a consistent 30% conversion rate from visitors to new customers. This means that for every 10 people who come to our store, 3 of them will become new customers. We attribute this success to our well-trained staff who are knowledgeable about our products and able to answer any questions a potential customer may have.
When it comes to repeat customers, we have found that 50% of our customer base are repeat buyers. These customers typically make purchases once a month and have an average purchase amount of . This is an important assumption for building our financial model, as it allows us to forecast our monthly income more accurately.
Tips & Tricks:
- Train your staff to know your products
- Offer promotions and discounts to encourage repeat business
- Collect customer data to track their buying patterns and create a more accurate financial forecast
By taking into account our conversion rate and repeat customer rate, we are able to create a comprehensive financial analysis of our business. This includes financial planning, forecasting, projections and managing our financial performance and metrics. It is essential for our success as a frozen food store to understand our financial statements and constantly make improvements to our profit model in order to continue to see our revenue growth.
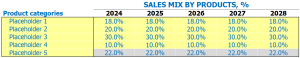
Frozen food store sales mix entrees
In our frozen food store, we sell a variety of frozen food products, all classified according to their type such as vegetables, meats, dairy products, bakery, etc. To better understand our sales mix, we created assumptions based on product category levers, which help us predict future sales.
Let’s take an example from our vegetable category. We have several products in this category, such as glazed carrots, broccoli, green beans, etc. To analyze the sales mix, we assumed that frozen carrots will represent 40% of total vegetable sales, broccoli will represent 30%, and green beans will represent the remaining 30%. We analyzed and entered the same assumptions for each product category based on historical data and current trends.
Our assumptions helped us create a clear and accurate picture of our sales mix, and we used this data to forecast sales for the next five years. Here are the sales mix percentages for the next five years for each of our five product categories:
- Vegetables: (Year 1) 40%, (Year 2) 39%, (Year 3) 38%, (Year 4) 37%, (Year 5) 36%
- Meats: (Year 1) 25%, (Year 2) 26%, (Year 3) 27%, (Year 4) 28%, (Year 5) 29%
- Dairy: (Year 1) 15%, (Year 2) 15%, (Year 3) 16%, (Year 4) 16%, (Year 5) 17%
- Bakery: (year 1) 10%, (year 2) 10%, (year 3) 10%, (year 4) 9%, (year 5) 9%
- Other: (Year 1) 10%, (Year 2) 10%, (Year 3) 9%, (Year 4) 10%, (Year 5) 9%
Tips & Tricks:
- Regularly review your sales mix assumptions and percentages based on changing trends, customer preferences, or new products.
- Use sales mix data to measure the performance of your product categories and make changes as needed to improve profitability.
- Include your sales mix data in your financial analysis and projections to ensure an accurate forecast.
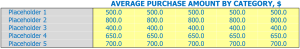
Frozen Food Store Average Selling Price
Our frozen food store offers a wide variety of frozen food products, each belonging to a specific product category. We found it easier to enter assumptions at the product category level than at the product level. For example, instead of estimating the average sale amount for each individual product, we can estimate it by category.
To do this, we entered assumptions about the average sales quantity of each product category, such as the average sales quantity of frozen vegetables, frozen pizzas, or frozen meats. We assumed that the average sale amount would increase by 2% each year, taking into account potential inflation and market trends.
Using the estimated average sale amount per category and our sales mix, we can then estimate the average ticket size. The sales mix represents the percentage of sales that each product category contributes to our total revenue.
For example, let’s say our sales mix looks like this: 40% of our sales are from frozen vegetables, 30% from frozen pizzas, and 30% from frozen meats. If we assume that the average sale amount for frozen vegetables is , frozen pizza is , and frozen meat is , we can calculate the average ticket size.
The formula to calculate the average ticket size is simply:
Average Ticket Size = (Sales Mix * Average Sales Amount of Each Product Category)
Tips & Tricks
- Regularly review and update your assumptions for average sales amount and sales mix to ensure financial forecast accuracy.
- Consider seasonal changes in the sales mix when estimating average ticket sizes.
- Consider implementing sales promotions or discounts to increase the sales mix and average ticket size.
Seasonality of frozen food store sales
Understanding the seasonality of sales is essential for the financial management of frozen food stores. This information is crucial for any financial analysis, forecasting and planning. The seasonality of sales helps the store owner estimate product demand at certain times and adjust inventory accordingly. When analyzing the seasonality of sales, we assume that there is a certain percentage of deviation from the monthly average sales per day.
For example, if the average sales per day in January is 0 and the variance factor is 10%, we assume that the actual sales per day will be between and 0. This way we can calculate the estimated earnings for each month and for the whole year.
Tips & Tricks:
- Use historical sales data to determine the variance factor for each month
- Plan promotional campaigns during slower months to increase sales
- Prepare a detailed financial statement that includes sales seasonality assumptions
When analyzing sales seasonality, we should pay attention to significant events that can affect product demand. For example, holidays, school breaks or weekends. It is essential to adjust the deviation factor accordingly. The frozen food store profit model should include consideration of these factors.
Financial forecasts and projections should include a detailed analysis of sales seasonality. Financial metrics, such as revenue growth or churn, should reflect sales seasonality assumptions. When considering the financial performance of a frozen food store, sales seasonality is one of the key factors to consider.
Frozen Food Store Operational Forecasts
Operational expense forecasts are an essential part of the frozen food store’s financial model. The forecast encompasses all costs it incurs in carrying out its day-to-day operations, including cost of goods sold by products %, employee wages and salaries, rent, lease payment or mortgage , utilities and other operating costs.
| Cost | Amount (per month) in USD |
|---|---|
| Cost of goods sold by products % | ,000 – ,000 |
| Salaries and wages of employees | ,000 – ,000 |
| Rent, lease or mortgage payment | ,500-,000 |
| Public services | ,000-,500 |
| Other running costs | 0 – ,000 |
| Total | ,000 – ,500 |
Frozen food store Cost of goods sold
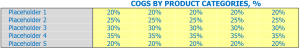
In a frozen food store, cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of production, including all costs associated with materials, labor, and overhead. For example, the cogs for a frozen pizza would include the cost of the dough, cheese, sauce, toppings, labor, and energy used to cook it.
COGS is usually expressed as a percentage of revenue and varies by product category. For example, the cogs for vegetables might be 30% while 60% for a prepackaged ready-to-eat meal.
Tips & Tricks:
- Minimize the cost of raw materials by sourcing from multiple suppliers or negotiating better rates.
- Automate the production process to reduce labor costs.
- Implement energy-saving practices in your store to reduce overhead.
Frozen Food Store Employee Salaries and Wages
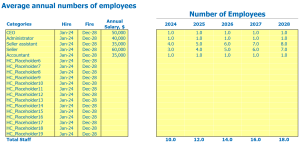
When it comes to frozen food store financial planning , wages and salaries of employees are an important factor. Hiring staff members will vary depending on the size of your frozen food store, location, and the type of business model you use. To effectively manage your employee’s costs, you need to plan ahead.
First, when you’re building a team, you should have a clear idea of what each role entails. Would you need a store manager, cashier, storekeeper or delivery driver? Create a list of staff members/positions you will need and distinguish between full-time and part-time roles.
Second, consider the level of experience required for each of these roles. A store manager, for example, may need years of retail management or business management experience under their belt. A cashier, on the other hand, may have a minimum requirement.
Third, it is important to hire seasonal staff during peak periods. This will allow you to avoid overstaffing staff during slow times and paying for staff that are not always utilized.
Finally, set realistic pay rates for your employees. Consider state and federal regulations that might affect how much you need to pay. You can also review frozen food store financial metrics to determine how much you can reasonably afford.
Tips & Tricks:
- Use job postings that outline the responsibilities and experience required for each position.
- Offer competitive salaries to attract employees with experience or qualifications.
- Calculate the number of employees you need at any given time to maximize profitability and minimize costs.
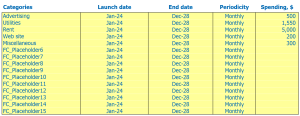
Frozen Food Store rent, lease or mortgage
When creating a financial plan for a frozen food store, one of the most important factors to consider is the cost of ownership. This can be in the form of rent, lease or mortgage payments.
Rent: If the store rents a property, the monthly rent payment will be a recurring expense. Cost may vary based on location, square footage and other factors. For example, a frozen food store in a prime downtown location will likely have higher rent costs than one on the outskirts of town.
Lease: A lease is a long-term agreement between the store and the landlord. Unlike rent payments, lease payments are generally fixed for the term of the lease. This can provide more stability when it comes to budgeting and financial forecasting.
Mortgage Payment: If the store owns the property, they will be responsible for paying the mortgage. These payments can also vary depending on interest rates and the term of the loan.
Tips & Tricks:
- Consider negotiating rent or tenancy agreements to get better terms.
- Tive to take potential increases in rent or mortgage payments when creating financial projections.
- If possible, avoid taking on more debt than the business can afford to repay.
Frozen Food Store Utilities
Utilities are an essential element to consider when we talk about frozen food store financial planning and performance. Utilities are expenses for electricity, water, heating, and cooling. Financial analysis of frozen food stores Can help you determine how much you should allocate to these services and use them effectively to avoid unnecessary expenses.
Assuming your frozen food store revenue model is based on a 2,000 square foot store, you can expect to pay ,000 to ,500 per month for electricity, 0 to 0 for heating and cooling expenses, and an additional 0 to 0 for water bills. However, costs may vary depending on your store location, weather and time of year.
Tips & Tricks
- Investing in energy efficient equipment can help you save money on utilities.
- Monitoring your usage and setting limits can help you reduce your expenses in the long run.
To build accurate Frozen Food Store Financial Projections and Frozen Food Store Financial Statements , you need to consider utility costs over time because they can add up and impact the frozen food store’s profit model. frozen food . Thus, it is crucial to negotiate and compare utility prices with different providers and seek out the most affordable and environmentally friendly options on the market.
Overall, to be successful in the long term, it is essential to prioritize frozen food store financial management and performance in all aspects, including utility expenses.
* No frozen foods were harmed in the making of this chapter.
Frozen food store other running costs
When creating a financial model for a frozen food store, it’s important not to overlook the other running costs that come with running the business. These fees may include expenses such as insurance, rent, utilities, and equipment maintenance fees.
For example, if the store has a freezer that needs regular maintenance, this cost should be included in the financial projections. In addition, rental and utility costs should be factored into the frozen food store financial statements to accurately predict store costs and profits.
To ensure accurate financial forecasts, it is important to include all costs associated with operating the frozen food store in the Frozen Food Store Financial Analysis and Financial Planning section . Only then can a Frozen Food Store Revenue Model and Frozen Food Store Profit Model be created that truly reflects the financial management and performance of the store.
Frozen Food Store Financial Forecasts
When it comes to the financial model of a frozen food store, a critical aspect is provided. Financial forecasting involves creating predictions of future financial trends and evaluating the estimated results. The forecasting process includes several documents that include profit and loss statement, sources and uses of funds, and cash flow analysis. Accurate forecasts are fundamental in the development of financial planning, projections, analysis and performance metrics to measure the financial performance of the frozen food store.
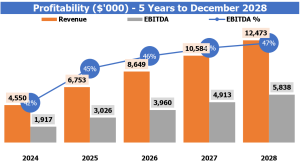
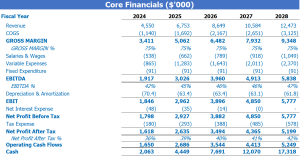
Profitability of Frozen Food Stores
Once a frozen food store has built its revenue and expense projections, the next step is to analyze the financial statements to understand the profitability of the business. The Profit and Loss (P&L) statement is a great vantage point to start understanding the overall financial condition of the store.
The P&L will provide insight into many financial metrics, including gross profit or EBITDA margin. These two metrics are ideal for understanding the efficiency of frozen food store operations. Understanding gross margin is important because it tells us how much money is left over after covering variable costs such as food, labor, and packaging costs.
Tips & Tricks
- Analyze your frozen food cost to understand if you have an efficient ordering process in place.
- Keep track of labor costs with a scheduling system to control salaries.
- Keep an eye on packaging costs and negotiate better rates with suppliers where possible.
Ultimately, understanding the financial performance of a frozen food store is critical to making informed business decisions. By performing regular analysis and creating financial projections, a store owner can stay on top of any changes in their financial performance and make adjustments if necessary.
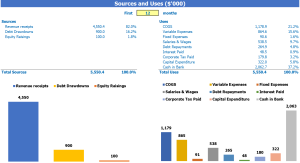
Sources and use of frozen food stores
The Sources and Uses of Funds in Financial Model in Excel for Frozen Food Store provides users with an organized summary of where capital will come from Sources and how that capital will be spent in the Uses . It is important for the total amounts of sources and uses to be equal to each other. Disclosure of sources and uses is particularly critical when the company is considering or going through recapitalization, restructuring, or mergers and acquisitions (M&A).
Frozen Food Store Revenue Model Refers to the amount of revenue a store is able to generate. The Frozen Food Store Profit Model is important for understanding how much money a store will generate in the long run. Financial analysis of a frozen food store is important in understanding how profitable a store can be. Financial planning is necessary to ensure that the business operates with enough capital. Financial forecasting is useful for predicting future growth. Financial projections are estimates of future performance, based on past performance. The Frozen Food Store Financial Statements describes the financial condition of the business. Financial management can make or break a business. Financial performance is the measure of business success, and financial metrics help monitor that success over time.
Tips & Tricks
- Keep track of your sources and uses of funds to ensure proper financial management.
- Use financial metrics to track your frozen food store’s performance over time.
- Understand your frozen food store’s financials – these are key indicators of business success.
Building a comprehensive financial model is crucial to the success of any frozen food store. It helps predict future financial performance and identify areas that need improvement. The financial model includes the revenue and profit model, financial analysis, planning, forecasting, projections, statements, management, performance and metrics. With an effective financial model in place, frozen food store owners can make informed decisions that help drive the growth of their business. Therefore, it is essential to take the time to build a solid financial model to achieve the desired financial goals.